How to Check CPU Voltage Complete Guide 2023
Keep reading to know how to check the voltage of your CPU. There are two methods for measuring this: using a multimeter and using software that does it for you. Let’s take a closer look at each choice. Using Intel XTU and the datasheet, you can verify the core voltage of the i9-9900K.
Hardware or system monitoring tool is one of the most crucial pieces of software to have on any PC. Many people believe that this is only necessary for overclockers who push their hardware to its ultimate boundaries, but this is not the case.
I can’t tell you how many times individuals have asked me why their computer is operating so slowly or why their laptop is randomly shutting down because they had no idea their system’s fan had died, and it was overheating.
Article Headings
How to Check CPU Voltage?
Well, this won’t happen to you because you’ll have access to a hardware monitoring program that will assist you in diagnosing any issues before entrusting your computer to a technician. The first step is to figure out which type of voltage measurement system your motherboard employs: Vcore or VRM. It most likely utilizes Vcore if it has an ATX power supply; if not, it most likely uses VRM (if it’s an older computer). So, have your multimeter ready!
Vcore and VRM
The voltage of V connections on motherboards is referred to as Vcore. The core of your CPU is Vcore, which is a voltage that comes from VCC IN. Here the voltage is where the CPU/GPU operates, and this is where most people get confused. What’s the difference between VCore and other voltages? How do you raise or lower a value? People frequently inquire about how to see Vcore or other voltages.
The Voltage Regulator Module (VRM) works in tandem with the motherboard’s BIOS to provide power to all the components. Different resistors on PCBs, which are large-scale integrated circuits that control voltages within your computer, are how VRM delivers voltage. The quality of your motherboard’s VRM determines how much power is provided to your CPU/GPU.
If you want to have a stable overclocking experience, a good VRM will assist you in doing so without having to worry about shorting out anything within your PC or raising temps above the permitted level.
Adjusting the VCore and VRM
Adjusting the VCore value in BIOS is the simplest technique to enhance VCore. What amount of money do you require? How much voltage can your CPU/GPU withstand? What is the maximum voltage that will boost performance? If you wish to modify these values, you should know how to check them.
A static or dynamic (dynamic load changes) vcore is available. The term “static” refers to the fact that the amount of voltage remains constant regardless of what happens. When a load is placed on the CPU, the voltage is increased until the PC reaches maximum throttle.
If you don’t know what you’re doing, don’t modify the voltages on any part (CPU core/RAM/NB) in BIOS. If you make any changes, make careful to test them for stability. We regret that we cannot be held liable for any damages.
How to Check CPU Voltage (With Motherboard BIOS)
- Find the jumper that selects your motherboard’s socket; it should be on pins 1, 2, or 3. (check your motherboard manual for details)
- Remove anything that may be obstructing the socket, such as a plastic bag or clothing.
- Unplug the computer from the power outlet and turn it off.
- Set the jumper to pins 2-3 (for reading voltages), then link the multimeter’s power cord into Pin 1 with the red lead wire; don’t forget to connect the black lead wire to a metal component of your computer case as well!
- Check your multimeter’s display for any voltage readings.
- Disconnect the power cord and reposition the jumper to pins 1-2 (for computer enablement), then reconnect the power cord and switch on the computer; you can now access BIOS settings.
How to Check CPU Voltage (With Software)
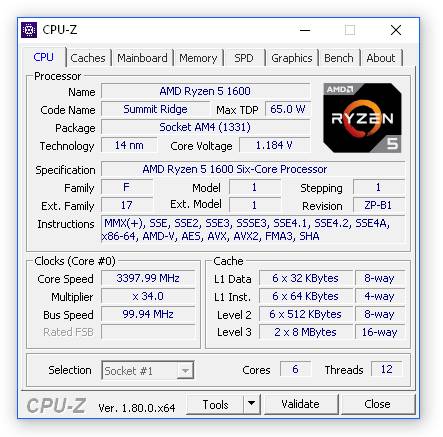
- Ascertain that your computer is linked to the internet (to access CPU-Z directly).
- Install the CPUZ software on your computer.
- Make that the utility tool you’re using lists all the voltage options available in your system BIOS, such as Vcore = 1.100 V. Vdimm = 2.000 V Vdimm = 2.000 V Vdimm = 2.000
- If there is a mismatch between these voltages and those provided by your motherboard manufacturer, look for another utility application or upgrade the present one due to a mistake!
Reduce Usage
- Use a low overclocking level, such as Vcore = 1.150 V, to avoid using excessive voltages.
- Make use of a high-quality power supply (PSU).
- Replace the factory cooling fan with an aftermarket cooler that can reduce CPU height temperatures while also lowering voltage consumption!
- In your system, only utilize one high-performance graphics card. Remove one of your graphic cards if you have two to minimize total heat, vibration, and noise caused by computer case fans and airflow restriction inside your case. It also aids in the reduction of CPU temperature and frequency rates!
Conclusion
Finally, there are a variety of reasons why you should monitor the voltage of your CPU. However, you must first learn how to do it to ensure that everything on your PC runs smoothly and properly.
How many times have you encountered a defective power supply or insufficient cooling? All of these difficulties could be resolved with a simple check of your CPU voltage! We hope that this post has clarified how simple it is to measure CPU voltage using these procedures.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
How do I know the voltage of my CPU?
- Vcore is the processor’s operating voltage.
- Using Intel® XTU (Intel® Xtreme Task Utility)
- Intel® Extreme Tuning Utility can be downloaded here.
- To configure the hardware monitor, open the utility and click the Configure Hardware Monitor icon in the lower-right corner.
- Close after selecting Core Voltage.
- The value of the core voltage will be shown in the lower-right window.
What is normal voltage for a CPU?
The core-voltage requirement is usually set by specific processor performance parameters and ranges from 0.9 to 1.3V. The most recent core-supply voltage tolerance requirements are usually around 3%. The issue of delivering reliable processor power is made significantly more difficult by the existence of large current transients.
What happens if CPU voltage is too low?
The CPU will not be affected if the voltage is set too low. The CPU will be damaged if the voltage is set too high. Overclocking the CPU, memory bus, and other components increases the base speed. This can’t go much higher without becoming unstable.









